Introduction to Dust
Introduction
Dust and Sand
The terms dust and sand usually refer to solid inorganic particles that are derived from the weathering of rocks. In the geological sciences, sand is defined as mineral (i.e. rock derived) particles with diameters between 62.5 and 2000 µm, whereas dust is defined as particles with diameters smaller than 62.5 µm (note that the boundary of 62.5 µm differs depending on particle size classification schemes). In the atmospheric sciences, Dust is usually defined as the material that can be readily suspended by wind whereas sand is rarely suspended and can thus form sand dunes and ripples, which are collectively termed bedforms.12
Aeolian Process
The wind-driven emission, transport, and deposition of sand and Dust by wind are termed aeolian processes, after the Greek god Aeolus, the keeper of the winds.
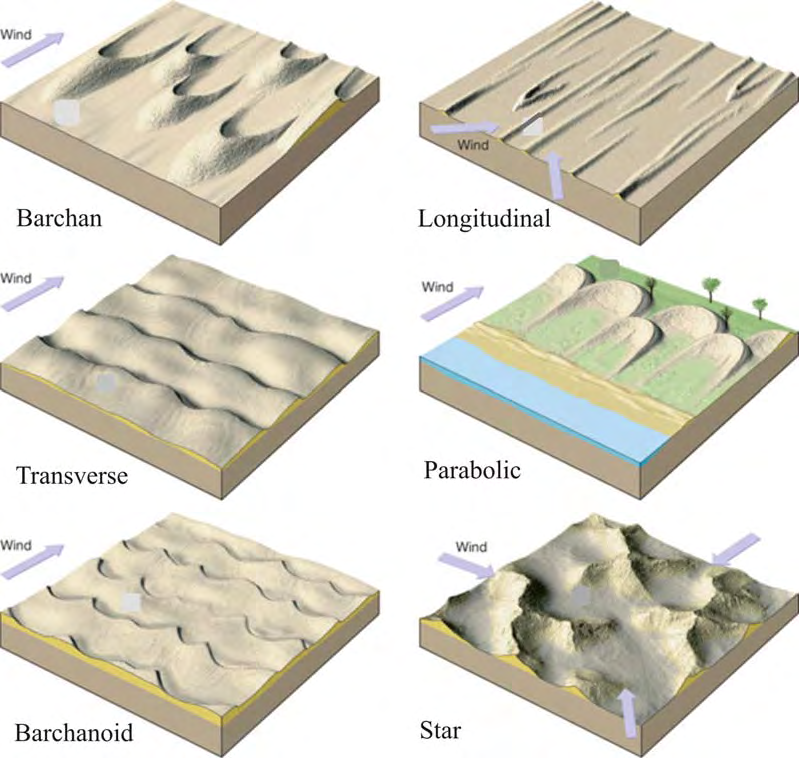
Sand Dunes
Kok, J. F.; Parteli, E. J. R.; Michaels, T. I.; Karam, D. B. The Physics of Wind-Blown Sand and Dust. Reports Prog. Phys. 2012, 75 (10), 106901 ↩︎
Michael E. Brookfield, 2011. “Aeolian processes and features in cool climates”, Ice Marginal and Periglacial Processes and Sediments, I. P. Martini, H. M. French, A. PéRez Alberti ↩︎